Similar to the internet in its early days, blockchain technology has experienced massive shifts in acceptance and use cases in a short span of time. The underlying technology to Bitcoin is being leveraged by large organizations to disrupt almost all operations and processes covering multiple industries.
Across financial services, supply chains, real estate, healthcare, and many other sectors, innovators have achieved significant benefits through blockchain. Enhanced security, greater transparency, decentralization, improved traceability, and reduced costs are amongst the primary benefits the technology tends to offer. However, the blockchain has struggled with certain challenges related to scalability and slow transaction speed in comparison to Visa or Mastercard. Several side chain and off-chain solutions, including the Lightning Network and EOS have been introduced to cope with the prevailing challenges.
If enterprises could augment blockchain’s advantages while addressing its scalability and latency issues, it could become the eminent business tool that could bring transformation changes to the world as the internet.
The day will soon come courtesy of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), the new and improved generation of blockchain.
Introduction to Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs)
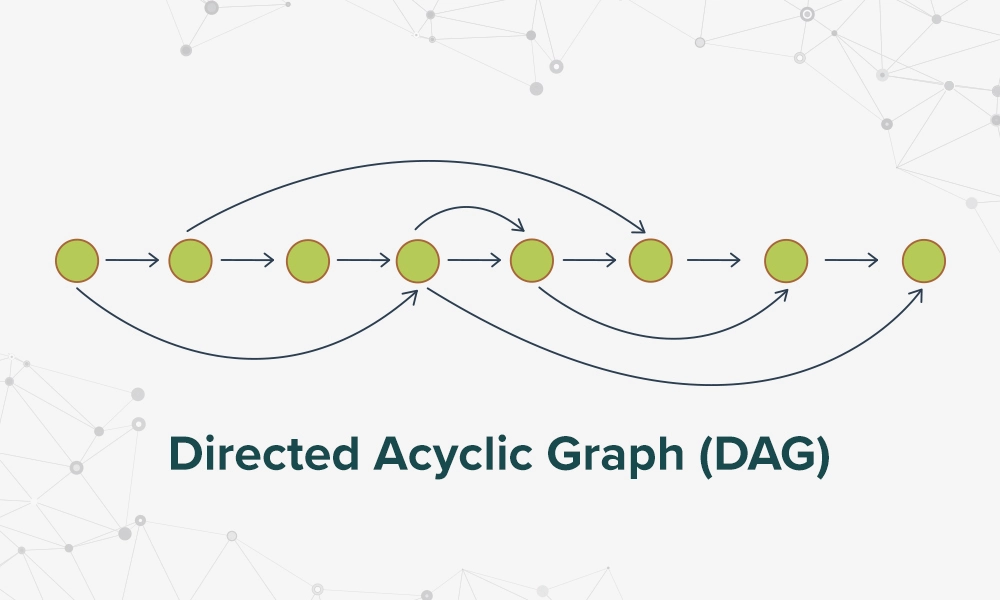
DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph. It is a directed graph data structure that uses a topological ordering. The technology is often placed together with blockchain, however, DAG is not technically similar to it. DAG is considered to be another form of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
DAG is a network of individual transactions linked to multiple other transactions that completely do away with blocks. Consider DAG as a tree, where transactions branch out from one to another, to another, and so on. The transactions are processed in sequences that can only go from earlier to later. Any new transaction needs to validate two previous transactions to become validated. The transactions are selected randomly by an algorithm to avoid bias amongst the members. This translates into instant transaction settlements and permanently low fees.
A single valid transaction can confirm many transactions in succession. That means, more transactions are processed, the quicker it will become to process more. This phenomenon ensures DAG is highly scalable and can work effortlessly in case of high traffic.
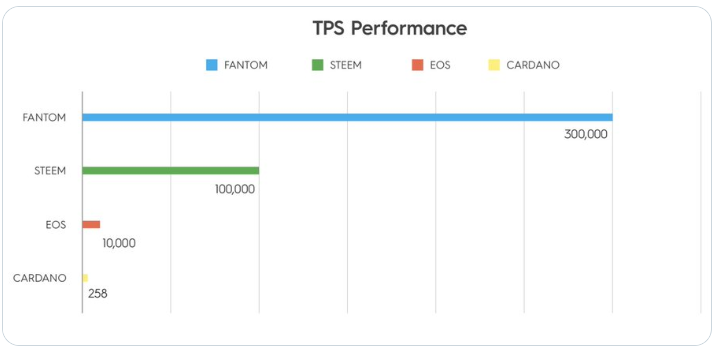
A Korean DAG startup, Fantom has tested its OPERA Chain to process up to 3,00,000 transactions per second — which is 12 times faster than Visa.
Benefits of DAG
DAG, an improved generation of blockchain, comes with significant benefits over the blockchain. Here are some advantages that DAG offers to the users:
- Instant transactions – There are no blocks in the DAG network. Thus, the transactions directly enter the network. It makes DAG faster than other networks that operate on PoS or PoW consensus.
- Scalability – With its infinite ability to scale, DAGs are well suited for high volumes of transactions. The higher the volume of transactions, the faster a DAG validates them.
- No mining – Unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchain, DAG has no miners. When a transaction is registered, it first has to validate two other transactions to become verified. Those transactions are chosen by an algorithm that removes the need for miners.
- Almost zero transaction fee – The fact that miners are eliminated from the network, network users validate transactions themselves, bringing down the transaction fees to almost zero.
- Lower energy consumption – As miners are eliminated, this, in turn, cuts out the need for mining equipment — meaning lower energy consumption.
Notable projects using DAG
IOTA

With its unique features and claims of eliminating the concept of a miner’s fee, the currency has gained immense popularity amongst industries. Using DAG (which it calls Tangle), IOTA aims to eliminate the need for blocks as well as miners, allowing for better scaling. For each transaction that happens in IOTA, the node which creates the transaction is required to approve two previous transactions by solving a low difficulty computation. The lack of transaction fees in IOTA also enables the users to conduct small transactions (nano payments) on the network.
Hedera Hashgraph

Hedera Hashgraph claims to be the world’s first fast and secure public ledger for decentralized applications (dapps). Also called as the ‘Blockchain Killer’, the Hedera Hashgraph is slated to be utilized in 7 innovative dapps across industries like finance, media and entertainment, and real estate.
Read more in our blog – Understanding Hashgraph Technology
Byteball
Another project is Byteball that uses DAG to avoid many of the issues related to blockchain. Byteball does not have a blockchain nor blocks.
Conclusion
DAG promises instant transaction settlements, zero transaction fee and high scalability. These are the reasons why many view it as ‘Blockchain 3.0.’ These are also the main drivers that increase the chances of adoption of DAG by enterprises.
However, it might be a little early to conclude how advantageous DAG could be. The technology is still new and untested. So, it remains to be seen if it is revolutionary enough to bring the change that it is intended for.

.jpg)