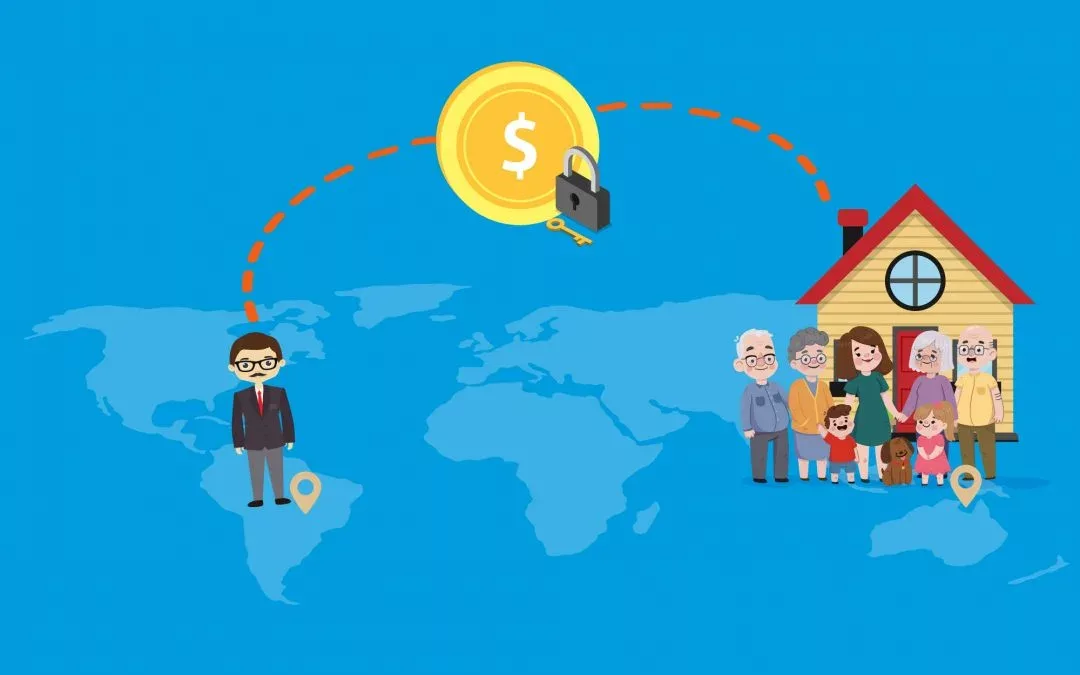
With industry globalization, it became easy for people to find work outside of their homelands. Especially in the developing countries, where it is difficult to find work and earn a decent income to meet the daily expenses, industry globalization was a game changer. However, as grabbing a job opportunity across the border for individuals became easy, sending the money back home (remittance pay) to support the family has turned difficult and expensive
For e.g. I am an Indian, working in America and when I transfer money back home to my family
a) it takes 3-4 days to transfer the money;
b) the banks charge 10-15% of the amount transferred and;
c) the exchange rate is 2.5-4% less than the market rate.
Individuals who are sending money back home every month aim to save every penny, but they are being crippled by the massive fees and long transfer periods. In many of the developing countries, the population around 50-70% don’t have access to a bank account or any financial service. An efficient system is needed in these countries to channel and manage the remittances. World Bank reports, the remittance payments in the low-to-middle income countries reached $466 billion in the year 2017 and is going to US $3323.4 million by 2025. From the above scenario what we can deduce is, there is a need of:
a) Regulated channels to send remittance at an affordable fee: The migrants are becoming more and more aware that there is a need of regulated channels to secure and fasten the money transfers.
b) Financial inclusion to offer good value proposition: Bank accounts and financial services, in general, are not friendly terms for the remittance senders and receivers. Therefore, there is a need of value proposition which connects with the concrete needs of these people.
c) Education for remittance pay: The remittance sender and receiver both rely on each other to gather information on the unregulated ways of sending and receiving money. As a result, both need to be educated to make informed decisions and safeguard money transfers.
Blockchain Technology in Remittance Pay
The expectations of Blockchain technology being incorporated in the remittance industry are quite high. As the blockchain technology is decentralized and transparent in nature, it can reduce the need of a middle-man such as established institutions. As a result, the remittance transfers will be done quicker with lower fees. The technology hands power back to the individuals – the individuals, in this case, are the ones who need it the most. We believe that the new technology opens huge opportunities. In general, trying to change an industry like this will take time and the companies driving these changes need
The experimentation in the sector has already begun with several banks and financial institutions around the world, looking at ways to use the new technology to simplify their banking and non-banking services. Various money transferring companies are also looking forward to utilizing the blockchain technology to initiate cross-border transactions which are easy, efficient and economical for the customers.
The paradigm shift seems to be coming from the non-financial organizations aiming to make money from this sector. For example in Europe the new PSD2 directive will challenge existing financial companies to adapt to the new situation and open up their services(APIs) to other companies. In December 2018, there were reports stating that the social media giant, Facebook entering to tap into the remittance market, enabled in Europe from the changes coming in PSD2. As reported by Bloomberg, Facebook is developing a cryptocurrency which will allow the users to transfer money through its messaging application, WhatsApp. The company is targeting the remittance market in India. The stablecoin, according to reports will be tied to $US dollar in order to avoid price volatility. Like many IT giants, Facebook is looking at ways to leverage the power of the decentralized technology.
For more information on PSD2, read our blog here.