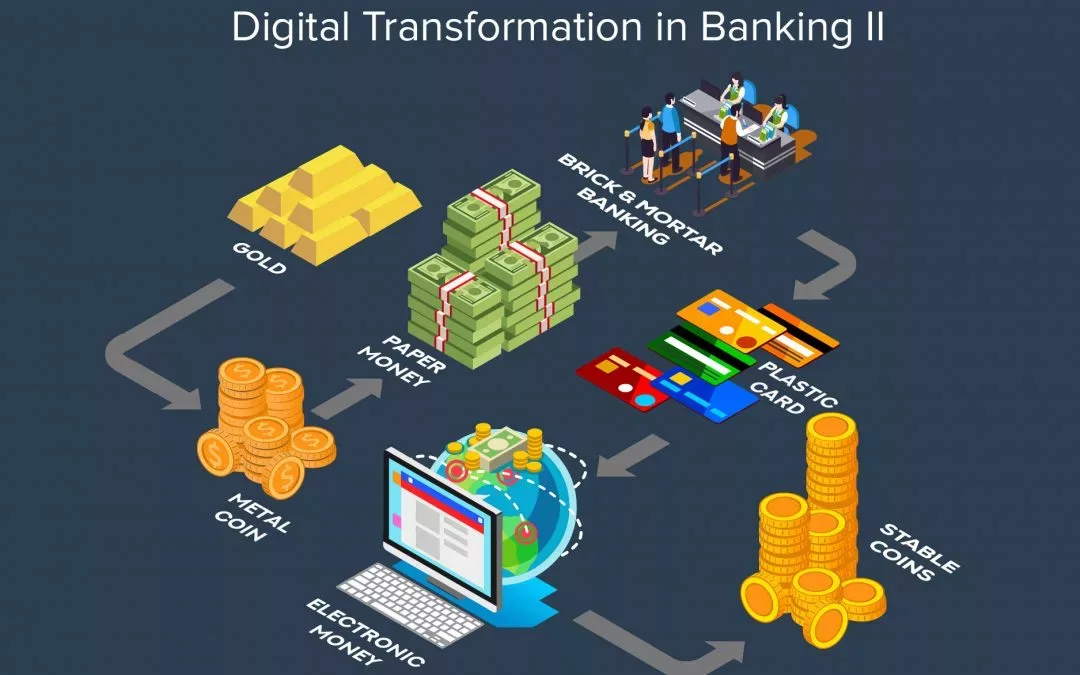
In the previous blog we discussed three trends out of seven driving digital transformation in the banking industry. Now let’s have a look at the four trends which are likely to change the face of the industry in times to come.
Cloud Computing
Even though the adoption of cloud computing in the banking industry is accelerating at a slow speed, it is still clear that the industry is moving towards this technology. With the kind of scalability cloud computing offers, banks can potentially scan thousands of transactions per second. This, in turn, enhances the industry’s ability to fight against financial crimes.
According to the Westpac, its new private cloud environment based on IBM Cloud technology is expected to make development ten times faster and three times cheaper. Let’s explore the benefits of cloud computing here:
- Agile innovation: By using cloud computing, banks can enhance their ability for digital transformation. As cloud computing increases agility, efficiency, and productivity by reallocating resources aside from the in-house IT administration, the banks can fast deliver products and services to the markets.
- Risk mitigation: The technology helps to reduce the risks associated with traditional technology like human error, redundancy as well as resiliency concerns. Also, cloud computing offers the ability for banks to be more equipped on issues such as frauds and money laundering.
- Cost-saving: With public cloud solutions, the banking industry is likely to have cost benefits in comparison to the traditional IT infrastructure, which required more capital-expenditure. During the peak-hours of customer demands, cloud computing can handle the capacity more efficiently. Moreover, with digital transformation and risk-mitigation, cost benefits are likely to arise as a result of the enhancement in technology.
Mobile Banking
The Payments Council has recently forecasted that the mobile banks are going to be used for 1.5 billion transactions by the year 2022. With this, one can easily imagine that the use of mobile technology is on an upward trend in the banking industry.
Banks currently are focusing on innovating the payments models and commerce capabilities on mobile platforms. The success of mobile banking is apparent from the data shared by CommBank, where online bank logins on the desktop were 88% three years ago but now they have come down to 44% (56% being mobile logins). In the UK, banks such as RBS, Barclays, HSBC, and Lloyds Banking Group have all developed their apps to enhance the shopping and payment modules for customers.
UK’s Office for National Statistics estimates that 20 percent of adult customers have made at least one mobile payment and 25 percent of bank customers use phones to check their balances.
Wearable technology
According to Samsung Insights, the future of retail banking is likely to be wearable technology such as smartwatches. For instance, the banks might use the Bluetooth tech to push forward personal messages to customer’s smartwatches when they enter the banking facility. Deloitte thinks that with digital transformation, companies will develop smart glasses which can quickly process customer account information for the bank teller. The smart glasses will work as an assistant for the bank employee and quickly churn information while he is busy doing other customer service tasks.
Wearable technology is all about learning from customer behavior and then advancing the banking industry in the direction of convenience. With the rise in the number of remote technologies, a customer is likely to interact with the bank from the palm of his hand. Moreover, from accessing banking online to visiting an actual branch, banking can offer a customer a whole new level of experience, more sooner than you may think.
Voice Over Technology
In the new future, most financial institutions are likely to move basic dialogue, account interaction to payments using voice commands. Industry experts say that in the next five years, around 50% of all banking related communications will be via voice-first-devices.
A significant portion of this digital transformation of voice-first is going to be an “intelligent assistant.” From the beginning, we have had experiences of interacting with maybe dozens of banking agents, each doing their own job, however, now it be the “ghost in the machine” who will be doing all the talking. These intelligent assistants will work in collaboration with an underlying banking software and form a secondary layer for you to connect with various banking services and systems.
A majority of the banking consumers are using the services for more than a decade; it is going to be exciting to watch the transformation.
Conclusion
Banks are assured that the development in technology will help them to deliver fast, safe, and customer-oriented services. However, regulations like PSD2, which has paved way from non-banks – or financial service providers to enter the market. It will only be seen in times to come that these cutting-edge financial technologies can help the bank to retain their customer or the tech-savvy customer is swayed towards these future-forward financial institutions.